by Raman Lab | Feb 19, 2025 | A physics of natural systems, Papers
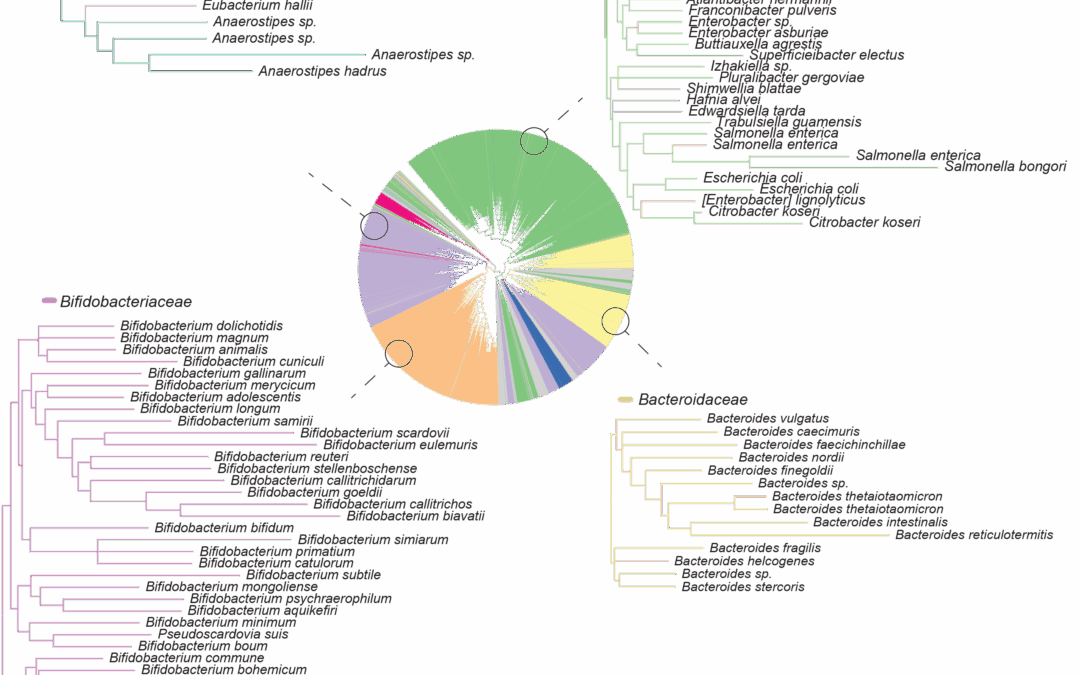
Subspecies phylogeny in the human gut revealed by co-evolutionary constraints across the bacterial kingdom With the advent of sequencing, biological systems like bacteria can be described in a myriad of ways, including by their entire genome sequence. But, with this...
by Raman Lab | Oct 22, 2024 | A physics of natural systems, Papers
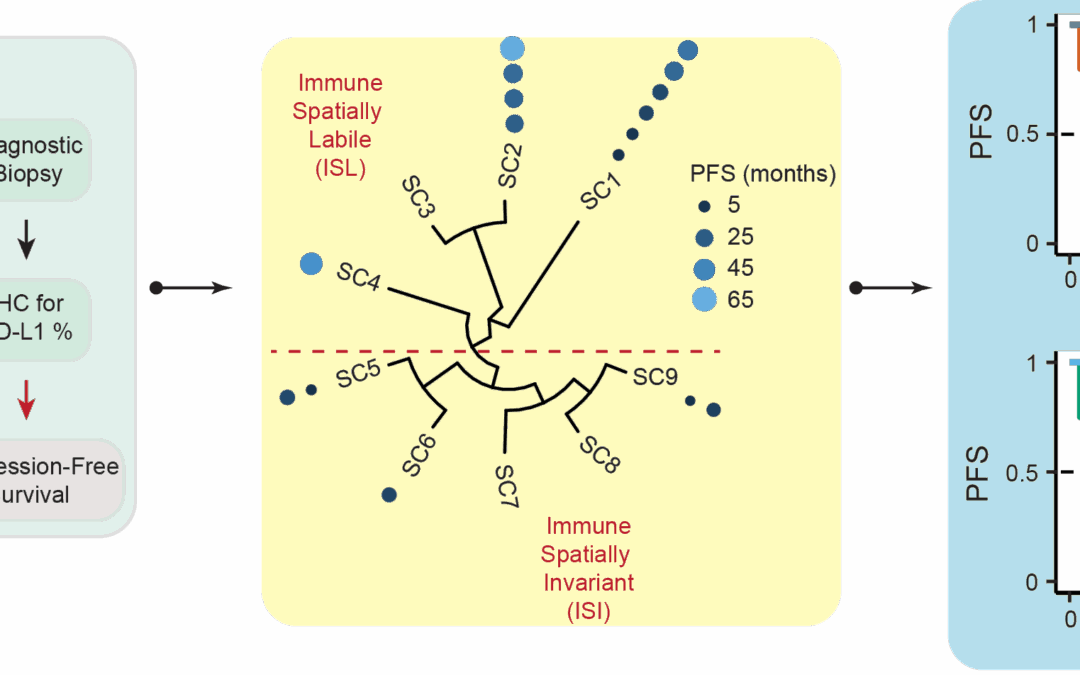
Conserved principles of spatial biology define tumor heterogeneity and response to immunotherapy Emergent phenomena are everywhere in biology—from macro-ecosystems like birds flocking and ants foraging down to the scale of ecosystems of amino acids that comprise a...
by Raman Lab | Aug 17, 2022 | A physics of natural systems, Papers
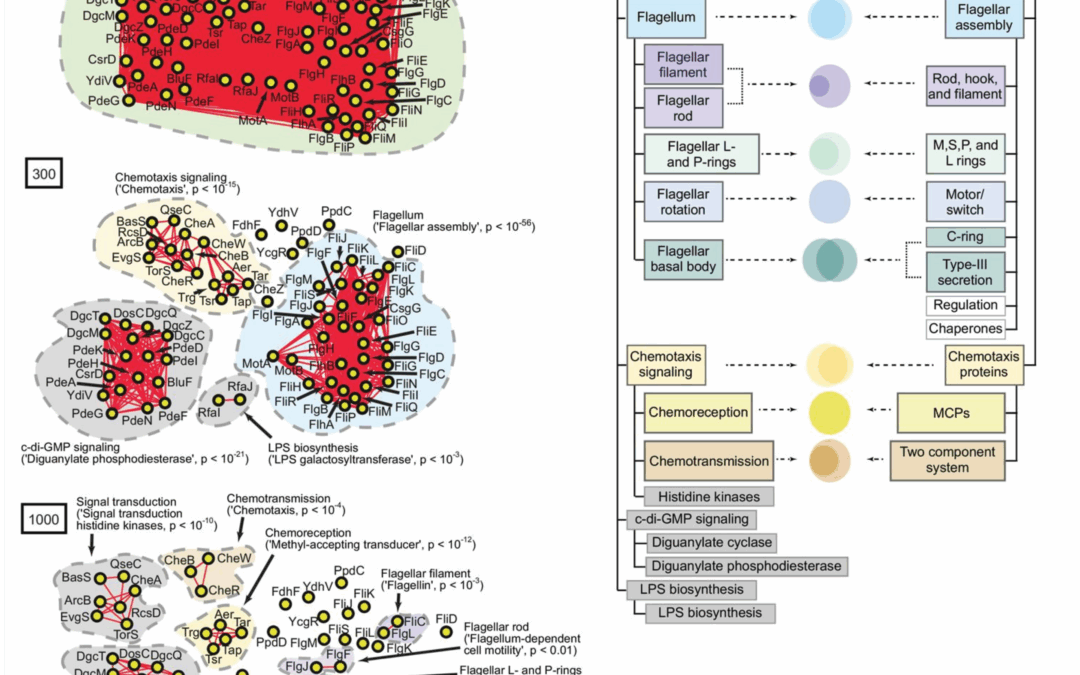
Defining hierarchical protein interaction networks from spectral analysis of bacterial proteomes If one were to buy a furniture set and accidentally lose the instruction manual, could we put the furniture back together? This is the question facing biologists all the...
by Raman Lab | Jul 12, 2019 | A physics of natural systems, Papers
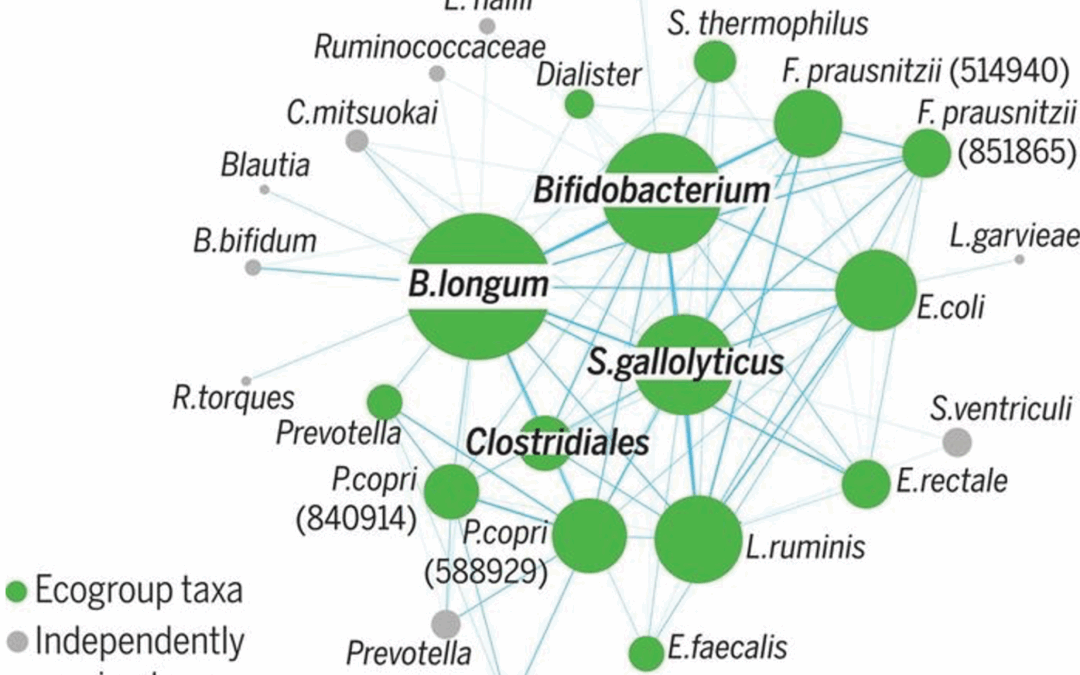
A sparse covarying unit that describes healthy and impaired human gut microbiota development The human gut microbiome is comprised of many species that all interact in strange ways so that we can be healthy and veer off disease. Given its importance, what is a good...

by Raman Lab | Jul 14, 2016 | A physics of natural systems, Papers
Origins of Allostery and Evolvability in Proteins: A Case Study Nature creates wonderfully complex micromachines known as proteins. While much effort has gone into understanding how these machines fold into compact structures and execute their function, little is...






